Primero te recordamos
que en inglés no existe la conjugación de los verbos como en español, donde
solo la conjugación en presente tiene 5 diferentes palabras, por ejemplo con el
verbo “hablar”:
Yo hablo, tú hablas,
ella habla, el habla, nosotros hablamos, ustedes hablan, ellos hablan.
En inglés solo tenemos el verbo “ TO SPEAK”
(el verbo con “to” es infinitivo): I speak, you speak, we speak, they speak. Peeero, cuando se trata de “he, she, it” sí se presenta una sutil
conjugación solamente agregando una “s” al verbo: she speaks, he speaks, it
speaks. SOLAMENTE EN LAS ORACIONES AFIRMATIVAS O DECLARATIVAS EN PRESENTE.
Veamos!
Ante todo hay que recordar que la palabra DO tienes dos (2) significados,
depende lo que tú quieras decir se usa como verbo principal o verbo auxiliar,
aclaremos:
Primero: DO como el verbo HACER, como verbo
principal en la oración. I do, you do, he do, they do (yo hago, tú haces, él hace, ellos hacen). Su
forma en pasado es DID y en pasado participio DONE, su presente participio
DOING.
1) La oración
AFIRMATIVA - AFIRMATIVE SENTENCE:
Recuerda que toda oración declarativa en inglés debe tener un sujeto y ese
sujeto seguido del verbo en su forma base (infinitivo sin “to”). “I to speak
English” se traduciría como tarzán: ”yo hablar inglés” y lo correcto sería “Yo
hablo inglés = I speak English”.
Quiero aclarar más lo de los
verbos en infinitivo, click.
Pero cuidado cuando se trata de la tercera persona del singular (HE,
SHE, IT) el verbo se conjuga agregando una “s”. Existen unas reglas para eso
que la agregamos mas abajo.
Nunca en la oración afirmativa aparece el auxiliar Do-Does, a menos que LA
INTENCIÓN AL HABLAR SEA dar bastante énfasis a lo que quieres decir.
Examples:
I do run every morning ( Yo SÍ corro todas las mañanas)
I do love you
(Yo SÍ
tea mo)
2)
La oración
INTERROGATIVA - INTERROGATIVE SENTENCE:
NO SE PUEDE
realizar pregunta en inglés sin primero colocar el auxiliar DO – DOES.
Determinado según el sujeto de quien se hable en la oración de la siguiente
manera:
Cuidado,
al preguntar sobre alguna tercera persona singular (HE, SHE, IT) al verbo no se
le agrega "s". La "s" ya la lleva el auxiliar
"DOES".
Cuando hacemos preguntas pidiendo información
dónde, cuándo, qué, cuál, como, igualmente se debe usar el auxiliar
correspondiente después de la palabra de pregunta (What, where, how, When, etc).
Si
escuchas algún hablante nativo, puede que no pronuncien el Do-does en inglés
coloquial, o puede que lo pronuncien tan rápido y corto que un oído extranjero
no lo percibe, pero en forma escrita siempre debe cumplir la estructura o
fórmula para preguntar del cuadro de arriba.
También se puede preguntar con negación de dos
formas:
1)
Con la contracción don’t – doesn’t
+ sujeto + verbo + complemento +?
2)
Auxiliar do- does +sujeto + NOT +
verbo + complemento + ?
Don’t they
dance?
Do they not
dance?
Doesn’t
Roger play chess?
Does Roger
not play chess?
Si
aún te confundes con los pronombres personales, de la primera a tercera persona
del singular y plural. Tenemos una publicación sobrelos pronombres personales aquí. CLICK.
3)
La oración
NEGATIVA - NEGATIVE SENTENCE:
NO SE EXPRESA UNA ORACIÓN NEGATIVA SOLO CON
“NOT” o “NO”. Debe emplearse el auxiliar DO-DOES de esta manera:
Las oraciones negativas se forman con el verbo auxiliar en forma
negativa: don’t-doesn’t, manteniendo invariable el verbo principal. Es decir,
ni porque se trate de una tercera persona (HE, SHE, IT) el verbo principal se
altera, no se le agrega “s”. Ya que el DOESN’T ya tiene la “es”, sería una
redundancia. Como decir en español “subir para arriba”, “entrar para adentro”,
je je je.
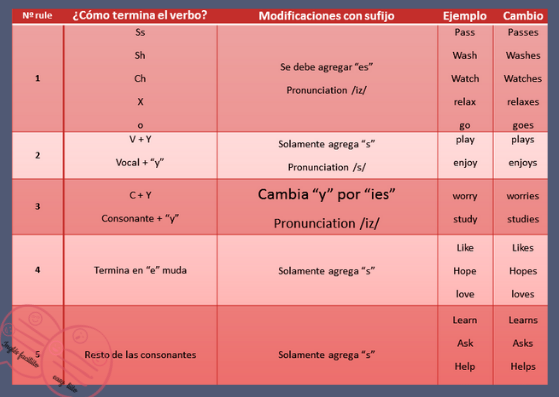
REGLAS PARA AGREGAR “s” A LOS VERBOS EN PRESENTE SIMPLE
Aquí te presentamos un cuadro que resume las
reglas para conjugación de los verbos en presente simple, cuya única
conjugación es agregar “s, es, ies” cuando se habla de una tercera persona del
singular (he, she, it).
NOTAS IMPORTANTES:
a)
A los verbos modales, como can, may, might o must, nunca se les añade una
–s NI AL VERBO MODAL NI AL VERBO PRINCIPAL. Se mantienen invariables en todas
sus formas.
b) b) El verbo to
be es irregular y SUPERPODEROSO en todas
sus tiempos. En las oraciones negativas e interrogativas NO SE UTILIZA EL VERBO AUXILIAR DO-DOES. El verbo to be tiene el
poder o facultad de él mismo poder hacer la pregunta y respuestas afirmativas o
negativas.
FREQUENCY ADVERBS/ ADVERBIOS DE FRECUENCIA
Los adverbios de frecuencia se utilizan con
el presente simple para dar un sentido de periodicidad a las acciones que se
realizan habitualmente, en cualquiera de sus usos como lo explicamos en el post sobre usos del presente simple. CLICK.
Algunos adverbios
de frecuencia son: Always, Usually, Often, Sometimes, Seldom, Rarely, Never.
COLOCACIÓN EN ORACIÓN AFIRMATIVA:
Examples:
My teacher often
understands me.
I am always hungry!
COLOCACIÓN EN ORACIÓN NEGATIVA:
Para negar usando un adverbio de frecuencia se
debe colocar DESPUÉS DEL AUXILIAR DO-DOES
Examples:
I don't always do the laundry.
You don't often get home before
8 pm.
He doesn't usually need his car.
She doesn’t frequently say bad
words.
COLOCACIÓN EN ORACIÓN
INTERROGATIVA
Colocación para preguntar usando un adverbio
de frecuencia: Igual que en la afirmativa, ENTRE EL SUJETO Y EL VERBO.
Examples:
Do you often
work at night?
Does she always take a nap in
the afternoon?
Does Peter never go to school?
Do they almost always come on
Christmas?
También existen otros adverbios de frecuencia,
éstos se pueden colocar al principio o al final de la oración. Tales como:
every + day / night / morning / afternoon...
Examples
Examples
1) Do you always believe things you
read in newspapers?
2) My father never drinks beer.
3) Does Roxy listen to the radio every
morning?
4) I never eat Chinese food.
5) Do your friends generally read an
English book in their free time?
6) What do you usually do to celebrate
your birthday?
7) What is something that a polite
person almost never does?
8) What does your mother often do after
work?
9) You are almost always friendly.
10) Is your girlfriend often romantic?
11) Do you generally take a shower at
night?
12) My cell phone is almost never in
service.
13) Are your parents usually busy?
14) Are Steven Spielberg’s films always
famous?
15) Do you often do exercise?
16) We always help our friends.
17) You sometimes put on too much
make-up.
18) I never say the truth.
Se suele preguntar con qué frecuencia haces
algo con… HOW OFTEN…?
How often do
you go out?
How often do
you read the newspaper?
How often are
you in charge in your office?
How often
do you go to the cinema?
How often
does she dance salsa music?
How often
does your grandmother listen to reageton?
How often
are you thinking in a past situation?
¿La has cantado?
Pues has cantado con muchas oraciones en presente simple, usando sujeto + verbo infinitivo sin to + complemento, adverbios de frecuencia, usando el verbo "to be" y el modal "can" en presente, la unión de 2 verbos con "to", etc.My heart will go on. Celine Dion
Lo resaltado en rojo son oraciones con presente simple:
Every night in my dreams
I see you, I feel you
That is how I know you go on
Far across the distance
And spaces between us
You have come to show you go on
Near, far, wherever you are
I believe that the heart does go on
Once more you open the door
And you're here in my heart
And my heart will go on and on
Love can touch us one time
And last for a lifetime
And never let go till we're gone
Love was when I loved you
One true time I hold to
In my life we'll always go on
Near, far, wherever you are
I believe that the heart does go on
Once more you open the door
And you're here in my heart
And my heart will go on and on
You're here, there's nothing I fear
And I know that my heart will go on
We'll stay forever this way
You are safe in my heart and
My heart will go on and on...
Te gustó esta publicación, COMENTA Y COMPARTE para que otros siguan aprendiendo inglés faciliiito y gratis. 👇👇👇












good
ResponderBorrarvery good!!!
ResponderBorrarBuena recopilación. ¡ Buen trabajo! Gracias
ResponderBorrar